A Game Courier Preset for Fairy Pieces Tester
Rules of Fairy Pieces Tester
All pieces and rules are the same as FIDE Chess with the exception of the following:
-Pawns may make a step on the first move up to 6 spaces. En Passant rules still remain the same, relative to the step adjustment.
-Draws occur at 100 moves with no capture or pawn move instead of 50.
-Castling occurs by moving the King to the C-file or O-file. Since there is no Rook, the King castles with the Wazir/Dababba Rider in the corners instead. The Wazir/Dababba Rider moves to the opposite side of the King in the castle and the distance moved is unchanged from how far a Rook moves during a castle in a standard game of Chess. All other stipulations of castling are the same, relative to the new piece.
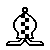
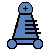
 Wazir / Dababba Rider - Moves 1 space orthogonally or jumps in a continuous orthogonal line 2 spaces. May leap over intervening pieces during the Rider movement.
Wazir / Dababba Rider - Moves 1 space orthogonally or jumps in a continuous orthogonal line 2 spaces. May leap over intervening pieces during the Rider movement.
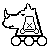
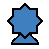
 Rose - A Circular Nightrider. Makes a series of continuous Knight moves, but must make a 45 degree turn with each leap. Like the Knight, it can jump over intervening pieces, and like the Nightrider, each square it actually comes into contact with must be empty.
Rose - A Circular Nightrider. Makes a series of continuous Knight moves, but must make a 45 degree turn with each leap. Like the Knight, it can jump over intervening pieces, and like the Nightrider, each square it actually comes into contact with must be empty.
 Crooked Bishop - Moves as a Bishop that must make a 90 degree turn with every step, and must of course always keep moving away from its starting square.
Crooked Bishop - Moves as a Bishop that must make a 90 degree turn with every step, and must of course always keep moving away from its starting square.
 Super Knight - Knight (1,2 leaper) / Camel (1,3 leaper) / Zebra (2, 3 leaper) compound.
Super Knight - Knight (1,2 leaper) / Camel (1,3 leaper) / Zebra (2, 3 leaper) compound.
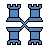
 Archbishop - Bishop / Knight compound.
Archbishop - Bishop / Knight compound.
 KnightRider - Moves as a Knight but may continue moving as a Knight in the same direction.
KnightRider - Moves as a Knight but may continue moving as a Knight in the same direction.
 Super Half-Duck - Moves 1 square diagonally or acts as a (3,0 leaper), (2,0 leaper), or (3,3 Leaper).
Super Half-Duck - Moves 1 square diagonally or acts as a (3,0 leaper), (2,0 leaper), or (3,3 Leaper).
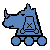
 Gryphon - Moves one square diagonal move and may continue outwards with a Rook move if it lands on an empty square.
Gryphon - Moves one square diagonal move and may continue outwards with a Rook move if it lands on an empty square.
How to Move Pieces
Full Algebraic Notation
Algebraic notation identifies each space by a coordinate that begins with its file label and ends with its rank label. On the Chess board, files go up and down from one player to the other, and ranks go from left to right. In most games, files are represented by letters, and ranks are represented by numbers, but there is no fixed rule requiring this for all games, and some games, such as Shogi, reverse this convention. If you look at the diagram, you will usually see the file labels going from left to right and the file labels going up and down. And if you hover your mouse over a space, you will normally see the name of the coordinate appear in a tooltip.
It is not uncommon to see algebraic notation being used for Chess, but it is often in an abbreviated format that requires you to know both the rules of the game and the current position to know exactly which piece moves where. For example, the notation "Ne6" indicates that a Knight is moving to e6, but it doesn't indicate which Knight, and it doesn't specify where the Knight is coming from. To figure this out, you need to know how a Knight moves and which Knight on the board can make a legal move to e6.
Although rules may be programmed for individual games, Game Courier itself does not know the rules of any game, and it is unable to parse abbreviated algebraic notation. Therefore, it relies on full algebraic notation, which completely specifies the move without requiring any knowledge of the game's rules or the current position. The most usual type of full algebraic notation indicates the piece that is moving by its label, the space it is moving from, and the space it moving to. In Chess, a typical first move might be written as "P e2-e4". When you hover your mouse over a piece, you will normally see the piece label followed by the coordinate for the space, and when you hover it over an empty space, you will normally see the coordinate label. Including the piece label in your notation allows Game Courier to check that the piece you're moving is the right one, and it makes game notation easier to follow, but it is not mandatory.
You may promote a piece by including a promotion move after your regular move. A promotion move has a piece go directly to a coordinate. Here is an example: "p e7-e8; q-e8".
You may remove a piece from a space by adding an @ to the space or by omitting the destination coordinate. For example, both "@-e4" and "e4-" would remove the piece on "e4". This is useful for en passant when you are playing a game that does not handle this automatically. For example, "P d5-e6; e5-" removes the Pawn on e5 after a Pawn moves from d5 to e6.
You will not need to remove spaces for most games, but if you should need to, you can do this by omitting the first coordinate in a move. For example, "-e4" would remove e4 from the board. To add or return a space to the board, you may add an @ or any other piece to it.
Available Pieces
Pieces are represented by labels, usually using uppercase letters for White and lowercase letter for Black. When you enter a move or specify the starting position for a game, you should remember that piece labels are case-sensitive. Many piece sets are available for use with Game Courier, and this table shows you which pieces belong to the piece set you are currently using.
These pieces come from a set containing more pieces, but this preset has had the set of pieces reduced to those used in the game.
















Credits
This preset uses the default1 settings file for Fairy Pieces Tester, which was made by Carlos Cetina.
Game Courier was created, programmed and written by Fergus Duniho.
Game Courier, Copyright © Fergus Duniho, 2001-2017
WWW Page Created: 15 August 2001


